13-CHAIN-OF-RESPONSIBILITY
责任链模式 #
描述 #
顾名思义,责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern)为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链。这种模式给予请求的类型,对请求的发送者和接收者进行解耦。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
在这种模式中,通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。如果一个对象不能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下一个接收者,依此类推。我们创建抽象类 AbstractLogger,带有详细的日志记录级别。然后我们创建三种类型的记录器,都扩展了 AbstractLogger。每个记录器消息的级别是否属于自己的级别,如果是则相应地打印出来,否则将不打印并把消息传给下一个记录器。
UML #
代码实现 #
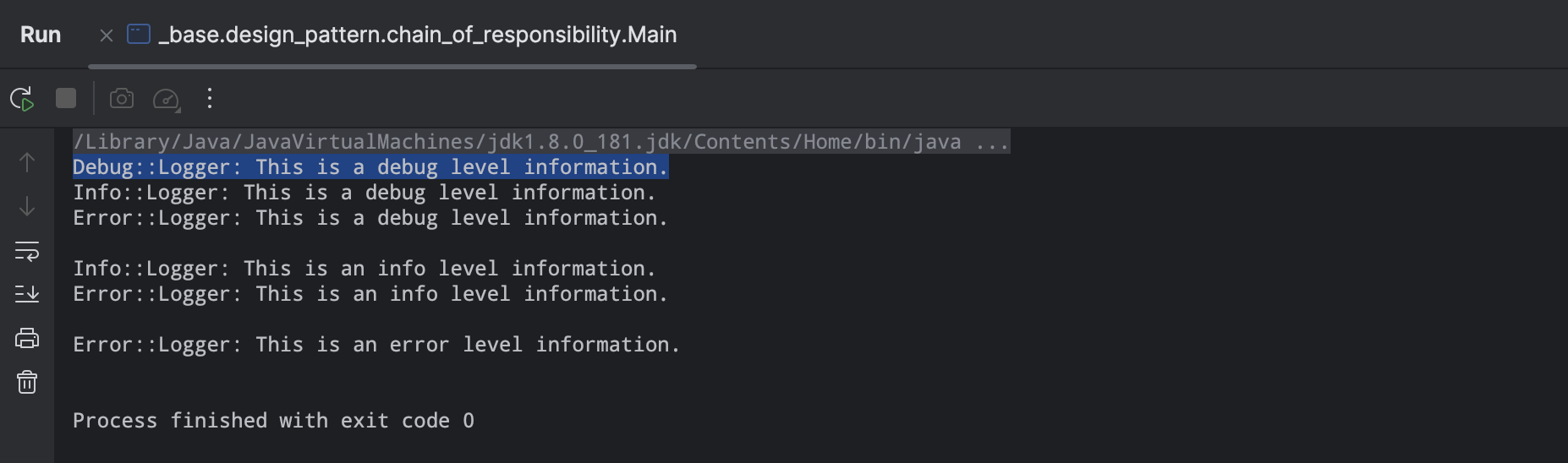
Reference #
comments powered by Disqus